

There are two exceptions to the processes mentioned above, which are the postganglionic neurons found in the sweat glands and the chromaffin cells found in the adrenal medulla. Stimulation of these target receptors result in the characteristic fight-or-flight responses. The postganglionic neurons in turn release a hormone called norepinephrine, which targets adrenergic receptors on various organs and tissues. Preganglionic neurons synapse with ganglia and release a chemical (neurotransmitter) called acetylcholine, which activates receptors on the postganglionic neurons. The preganglionic neurons have short fibers that originate from the spinal cord's thoracolumbar segments, which communicate with ganglia adjacent to the spinal column, and synapse with the longer postganglionic neurons. There are two types of neurons: the preganglionic neurons and the postganglionic neurons. Transmission of signals in the system is accomplished through a network of nerve cells called neurons. The Structure of the Sympathetic Nervous System The parasympathetic system enables you to maintain normal functions such as digesting and keeping the body at rest. The primary function of the sympathetic system is to stimulate your fight-or-flight response which is a physiological reaction that happens in response to a perceived harmful event, attack or threat to survival. It consists of the sympathetic and parasympathetic nervous systems. While your brain, which is a vital part of the central nervous system, has the capability to control your conscious actions like walking, thinking and talking, your body also has an autonomic nervous system, which regulates your bodily functions, like the beating of your heart, your breathing, the way you digest your food, your sweating patterns, etc.

This fight-or-flight response is brought about by your sympathetic nervous system, which usually helps you deal with stress.
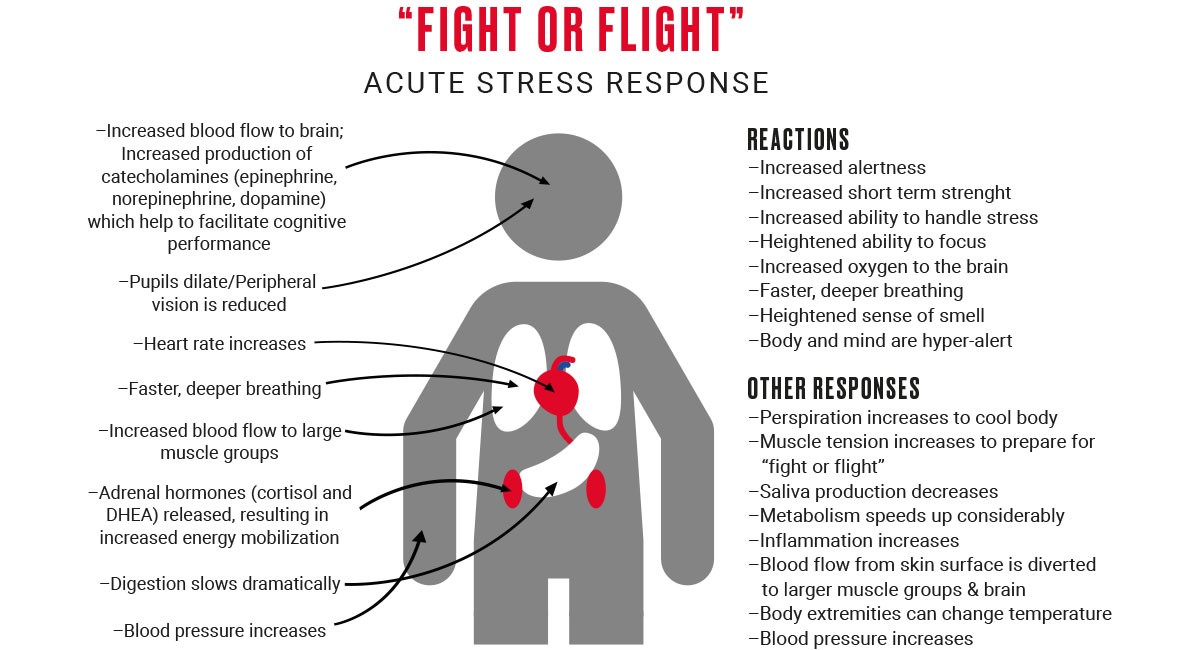
How does your body respond to stressful situations? Have you ever wondered why your heart suddenly beats rapidly and you break out into a sweat when you encounter some form of danger? It's almost an automatic response that occurs whenever you sense a threat, whether it is just a potential embarrassing situation or a really scary situation such as an attack by a stranger.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
